what is RAG
Introduction to RAG
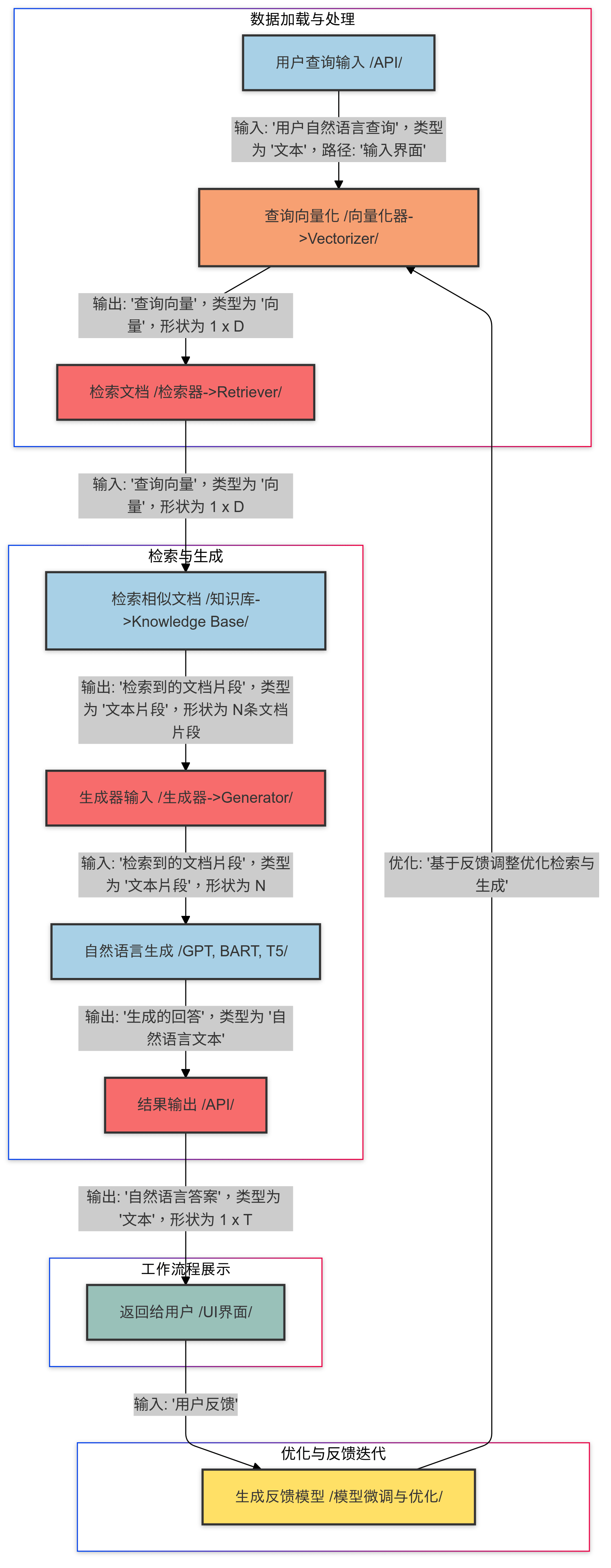
RAG is a hybrid architecture that combines information retrieval with generative models. First, the retriever acquires content fragments relevant to the user's query from an external knowledge base or document collection. Then, the generator produces natural language output based on these retrieved contents, ensuring that the generated content is both information-rich and highly relevant and accurate.
The RAG model consists of two main modules: the Retriever and the Generator. These two modules work in coordination to ensure that the generated text not only incorporates relevant external knowledge but also features natural and fluent language expression.
Working Principles of the RAG Model
Retrieval Phase
In the RAG model, the user's query is first converted into a vector representation, and then vector retrieval is performed in the knowledge base. Typically, the retriever uses pre-trained models such as BERT to generate vector representations of queries and document fragments, and matches the most relevant document fragments through similarity calculations (e.g., cosine similarity). Instead of relying solely on simple keyword matching, RAG's retriever adopts semantic-level vector representations. This enables it to more accurately find relevant knowledge when faced with complex questions or ambiguous queries. This step is crucial for the final generated answer, as the efficiency and quality of retrieval directly determine the contextual information available to the generator.
Generation Phase
The generation phase is the core part of the RAG model, where the generator is responsible for producing coherent and natural text responses based on the retrieved content. Generators in RAG, such as models like BART or GPT, combine the user's input query with the retrieved document fragments to generate more precise and comprehensive answers. Compared with traditional generative models, RAG's generator can not only produce fluent responses but also provide more fact-based content based on actual information in external knowledge bases, thereby improving the accuracy of generation.
Multi-turn Interaction and Feedback Mechanism
The RAG model can effectively support multi-turn interactions in dialogue systems. Each round of queries and generated results serves as input for the next round, and the system gradually optimizes the context for subsequent queries by analyzing and learning from user feedback. Through this cyclic feedback mechanism, RAG can better adjust its retrieval and generation strategies, making the answers generated in multi-turn dialogues increasingly aligned with user expectations. Additionally, multi-turn interaction enhances RAG's adaptability in complex dialogue scenarios, enabling it to handle cross-turn knowledge integration and complex reasoning.
RAG workflow